
Smart home devices are becoming increasingly popular, leading to a growing demand for secure and robust operating systems tailored for Internet of Things (IoT) environments. This article explores the rise of Linux-based smart home operating systems, highlighting recent developments and the various packages available for smart home applications. We will also discuss how Linux enhances the integration and management of IoT devices in the home.
The Growing Demand for Smart Home Operating Systems
Smart homes have rapidly evolved in recent years, driven by advancements in IoT technology, increased connectivity from new technologies, and consumer demand for convenience and automation. Today, smart home products include thermostats for climate control, lighting devices, security cameras, door locks, and voice assistants – all of which can be integrated, interconnected, and controlled remotely via smartphones, tablets, and computers.
Smart home devices have undoubtedly improved the comfort and convenience of modern living, but they also pose challenges in system interoperability, security, and device management. Traditional operating systems like Windows and macOS are not designed to handle IoT systems, often involving low-power devices, real-time data processing, and distributed computing architectures.
The Role of Operating Systems in Smart Homes
Operating systems play a vital role in smart home technology by enabling communication, integration, and coordination between devices. OSes offer an interface to manage connected smart home devices, allowing users to monitor, adjust settings, and control their smart home environment.
Traditionally, big proprietary OSes like Apple’s iOS and Google’s Android have dominated the market, often paired with the companies’ hardware offerings and devices. These systems offer integration within their ecosystems but come with drawbacks such as limited options and vendor lock-in. In contrast, Linux-based platforms allow developers to modify and enhance the software to meet specific needs and preferences. The flexibility enables innovation and the creation of unique, tailored products for smart home systems.
Linux’s Open-Source Advantage
The past few years have seen a growing interest in Linux-based platforms for smart homes. Several advantages make Linux particularly suitable for IoT applications, including the following:
Open-source nature: The Linux OS kernel is open source, which offers several advantages over other operating systems. The open-source flexibility allows developers to create custom distributions and packages for diverse hardware architectures.
Modular architecture: Allows for tailored system configurations.
Scalability: Easily adapts to different sizes and complexities of systems.
Robust security features: Provides strong protection against vulnerabilities.
Versatility and flexibility: Supports a wide range of applications and devices.
The surge in open-source software adoption has also provided a wealth of community-driven tools, libraries, and frameworks for developing smart home applications.
Popular Linux-Based Smart Home Operating Systems
Several Linux-based tools and packages have garnered attention in the smart home market. These operating systems offer tailored functionality for working with IoT devices and automating everyday household tasks.
Home Assistant
Home Assistant is an open-source framework for managing home devices. Users can control and automate their smart home devices from a central, easy-to-use dashboard. Home Assistant supports various devices and protocols, making it compatible with popular smart home ecosystems like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Phillips Hue (a lighting application for smart lamps).
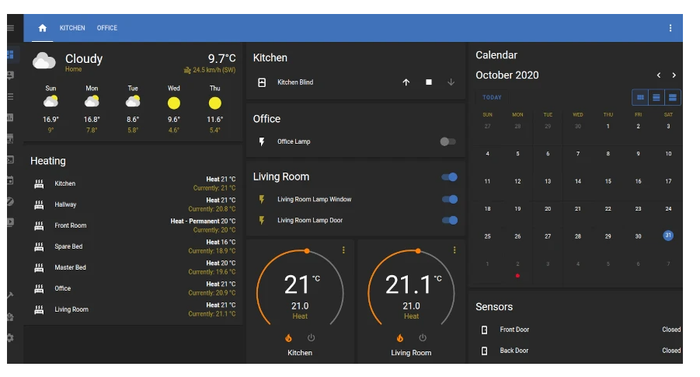
Credit: futurehousestore.co.uk
Figure 1. The Home Assistant dashboard.
OpenHAB
OpenHAB has functionality similar to Home Assistant but focuses more on flexibility and extensibility. Its modular architecture helps integrate devices, technologies, and services, from commonly used heating and lighting applications to weather forecasting and other monitoring and control systems.
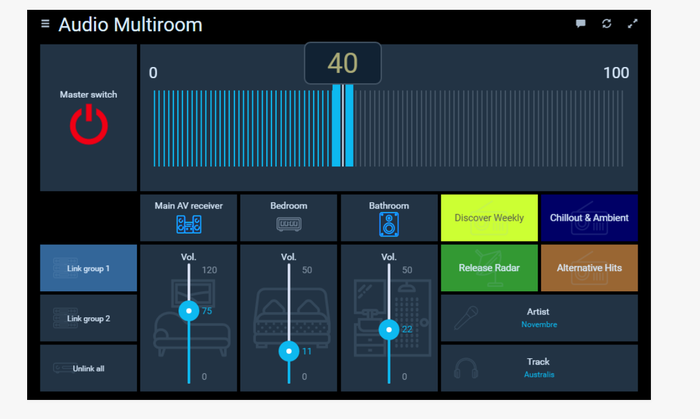
Credit: ubuntu.com
Figure 2. The OpenHAB user environment.
Domoticz
Domoticz is an open-source home automation system that lets users control lighting, switches, and meters, among other things. It is designed to operate cross-platform, with a user interface in HTML5 format, making it adaptable across different devices and platforms.
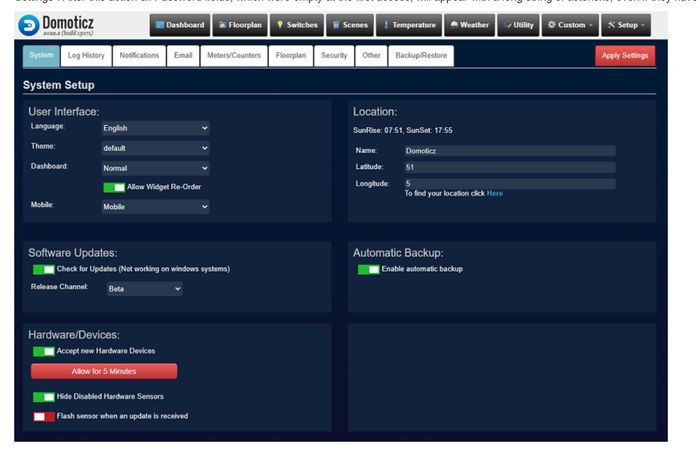
Credit: domoticz.com
Figure 3. The Domoticz user interface.
Integration and Management of IoT Devices
A key feature of Linux-based smart home operating systems and tools is their ability to integrate and manage IoT devices from multiple vendors using different protocols. The systems support standard IoT communication protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, and REST APIs. This capability enables interoperability between devices and platforms, allowing for a more cohesive smart home environment.
Linux-based home orchestration tools often include built-in support for device discovery technologies, as well as other configuration and management features that simplify the setup and administration of IoT networks. Users typically have access to an intuitive dashboard, enabling them to create rules for automating the monitoring and control of smart home devices, regardless of the manufacturer or protocol in use.
The Future of Linux-based Smart Home Operating Systems
Linux's open-source ethos and global community will foster innovation in the smart home space. Linux-based smart home operating systems, tools, and software packages will remain essential, while advancements in edge computing, machine learning (ML), and AI will enhance their capabilities, enabling more sophisticated automation and real-time decision-making.
Credit: engineersgarage.com
Figure 4. The Node-Red dashboard. Node-Red is an open-source tool from IBM that wires hardware devices.
Main Takeaways
Linux-based smart home operating systems and software tools represent a burgeoning frontier in smart home automation. The OSes provide users extreme flexibility, customization options, and precise control over their systems and devices. Supported by a vibrant global community of Linux enthusiasts, developers, and users, these platforms are primed to revolutionize how we manage and interact with smart home technology.
Additional Resources and Links
About the Author
You May Also Like








.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
