How to Gain Insight into Failed Login Attempts on WindowsHow to Gain Insight into Failed Login Attempts on Windows
An excessive number of failed login attempts can be a signal that a cyber attack is in progress.
October 12, 2021
One of the first security best practices Windows administrators learn is to audit failed login attempts. An excessive number of failed login attempts may signal a cyber attack, but simply knowing that an attacker is trying to gain access to user accounts isn’t enough to put a stop to the attack. You also need to know how the attacker is trying to get in. Windows provides this information, and this article offers guidelines for interpreting that info.
Event Log Entry for a Failed Login Attempt
You can access the Event Viewer by entering the Eventvwr command at the Windows Run prompt. When the Event Viewer opens, navigate through the console tree to Windows Logs | Security.
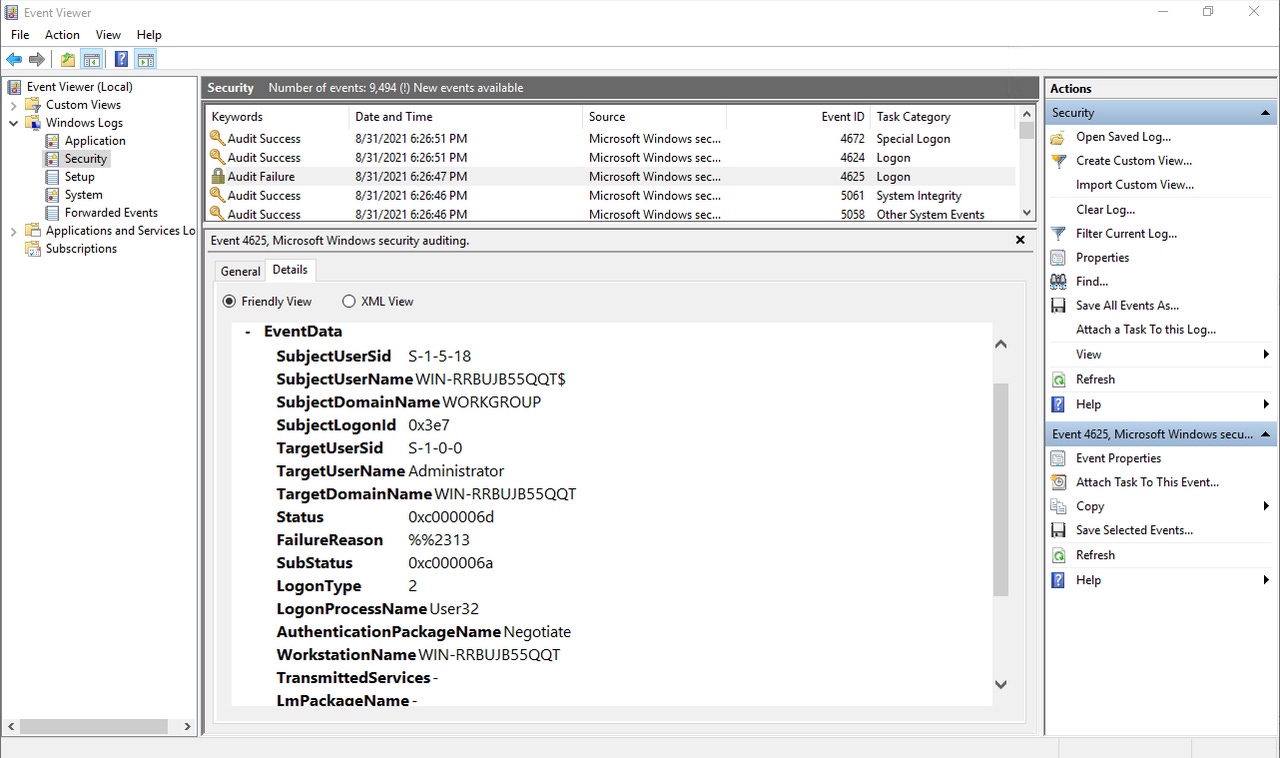
The Windows event logs assign an Event ID to each event. Event ID 4624 corresponds to a successful logon, whereas Event ID 4625 corresponds to a failed login. You can see what Event ID 4625 looks like in Figure 1.

Failed Login 1
Figure 1
Event ID 4625 is logged in response to a failed login.
As you look at the figure above, you can clearly see that an audit failure has occurred in response to an failed login. You can also see the date and time at which the event was logged, and that the user who attempted to login was using a workgroup account. This information alone is useful, but it is often possible to dig a little bit deeper and gain some additional insight.
One of the things that you might have noticed in the previous figure was that the area of the screen detailing the selected event contains two tabs: General and Details. If you select the Details tab, you can see additional information about the event, although much of this information can also be accessed through the General tab. You can see a lot of the event details in Figure 2.

Failed Login 2
Figure 2
These are some of the details that are logged in response to a failed login.
The Details tab includes information such as the name of the user account for which the login was attempted and the user’s SID. You can also see the domain name for which the login was attempted. In this case, the computer was not domain-joined, so the computer name is listed in place of the domain name.
Another thing that you might notice about the Details tab is that it provides a status and a sub status for the failed login. Unfortunately, both the Status and the Substatus fields are populated with hexadecimal data rather than a text-based description of the event. Even so, it is relatively easy to use these codes to figure out what is going on.
Failed Login Error Codes
Here are some of the codes that Microsoft uses:
0xC000006A - this code indicates that the username is valid, but that the user has entered an incorrect password.
0xC000006D – Either the username or password is incorrect.
0xC000006F - When this code is displayed it means that the organization has put into place time-based restrictions for logins, and the user has attempted to login outside of their allotted time. Some organizations, for example, will allow users to login only during business hours.
0xC000015B - This is an error indicating that the user does not have permission to login. Such an error might occur, for example, if a user lacks permissions to login locally.
0xC0000064 - Someone attempted to login using a username that does not exist. This can happen because an attacker does not have a list of valid usernames and is simply trying to login using common
0xC0000070 - This code often indicates that a user has attempted to login from an unauthorized device.
0xC0000071 - This error code means that the user’s password has expired.
0xC0000072 - This code indicates that the account the user tried to login to has been disabled by an administrator.
0xC0000133 - The Windows authentication process is based on Kerberos, which is a time-sensitive protocol. Kerberos authentication will fail and this code will be produced if the workstation’s clock is too far out of sync with the clock on the domain controller.
0xC0000193 - This error occurs when someone attempts to login using an expired account.
0xC0000224 - This code indicates that the login is allowed, but that the user is going to be required to change his/her password.
0xC0000234 - When this code is displayed it means that the user has tried to login to an account that is currently locked out.
In Figure 2, the event status is listed as 0xC00006D, which is a generic indication of a bad username or password. The sub status is 0xc00006A, which means that the password is incorrect. When you put all of this information together, it shows that someone has tried to log into this machine’s local administrator account, but used an incorrect password. If such an error is occurring consistently, it could be an indication that someone is trying to exploit the machine. It, therefore, might be wise to disable the local administrator account or assign it a more secure password.
About the Author
You May Also Like








.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
